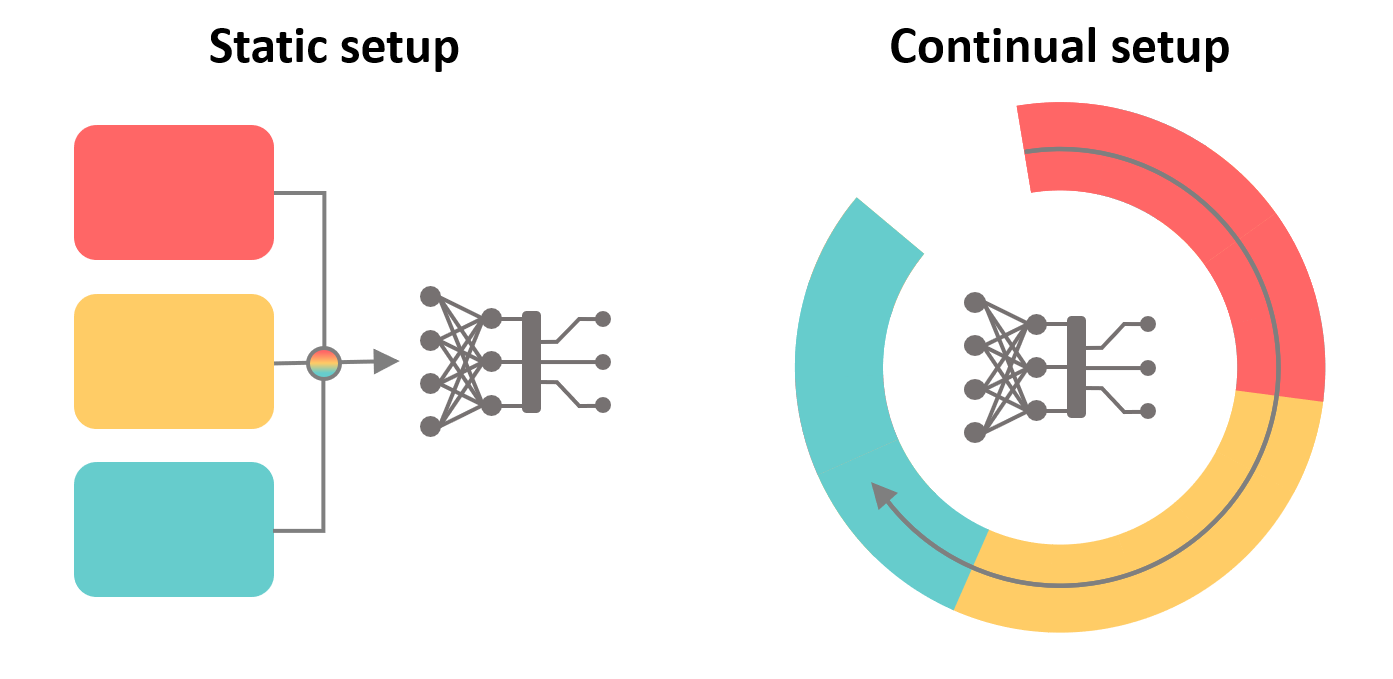
The usual workflow in the implementation of artificial intelligence methods consists of 1) training the model 2) evaluation and 3) deployment. Annotated data is shuffled and divided into training and test data. This workflow does not take into account that some training data might become available during deployment.
Continual learning means the sequential reception of small amounts of data from different sources. In contrast to the usual workflow, continuous learning algorithms can process successively incoming data, which may be available only for a short period of time. They perform well on all data observed during training, regardless of when this data was used to train the system.